When your body activates your immune system, it sends out inflammatory cells. These cells attack bacteria or heal damaged tissue. If your body sends out inflammatory cells when you’re not sick or injured, you may have chronic inflammation. Inflammation is a symptom of many chronic diseases, like arthritis and Alzheimer’s disease.
When something foreign enters your body (like viruses, bacteria or toxic chemicals), or you’re injured, your immune system activates. Your immune system sends out cells to trap bacteria and other offending agents or start healing injured tissue.
This is the inflammatory response. The result can be pain, swelling, bruising or redness. But inflammation also affects body systems you can’t see.
There are two types of inflammation:
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
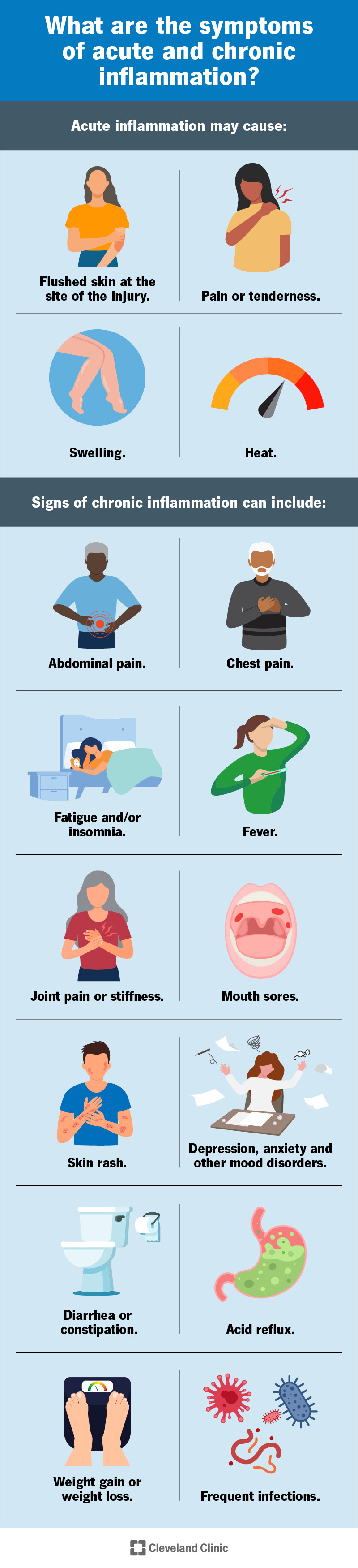
Acute inflammation may cause:
Chronic inflammation symptoms may be harder to spot than acute inflammation symptoms. Signs of chronic inflammation can include:
Chronic inflammation is involved in the disease process of many conditions, including:
Advertisement
The most common reasons for chronic inflammation include:
Some lifestyle factors also contribute to inflammation in the body. You may be more likely to develop chronic inflammation if you:
Inflammation doesn’t always require treatment. For acute inflammation, rest, ice and good wound care often relieve discomfort in a few days.
If you have chronic inflammation, your healthcare provider may recommend:
Advertisement
You may choose to eat more foods that have anti-inflammatory properties. Some research shows that people who follow a Mediterranean diet have lower levels of inflammation in their bodies.
Foods that reduce inflammation include:
Eating too much of certain foods may increase inflammation. If you have chronic inflammation, you may feel better if you avoid foods that cause inflammation, including:
You may decrease your risk of chronic inflammation by developing healthier lifestyle habits. Some of these habits include:
Check in with a healthcare provider if you experience a worrisome injury. Also talk with a provider if you have ongoing pain, swelling, stiffness or other symptoms. A healthcare expert can narrow down the cause and find ways to help you feel better.
Inflammation is an essential part of your body’s healing process. It occurs when inflammatory cells travel to the place of an injury or foreign body like bacteria. If inflammatory cells stay too long, it may lead to chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is a symptom of other health conditions, like rheumatoid arthritis. Your healthcare provider may recommend medication or at-home management. You can reduce inflammation by eating anti-inflammatory foods and managing stress.
Last reviewed on 12/20/2023.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy