Thanatophoric dysplasia is a rare, life-threatening genetic condition that affects the growth and development of a fetus’ bones and lungs. As a fetus’ lungs don’t develop completely in the uterus, breathing complications like respiratory failure are possible. Most babies are stillborn or die during early infancy. Support is available to families to grieve the loss of their child.
Thanatophoric dysplasia is a genetic condition that affects the development of a fetus’ bones and lungs.
The term “thanatophoric” is ancient Greek for “death bearing.” This is because many children are stillborn or die during or shortly after birth due to breathing problems/respiratory failure because of lung underdevelopment before birth.
Rarely, a child with this condition may survive into childhood with extensive treatment to address respiratory failure. Respiratory failure happens when there’s not enough oxygen or too much carbon dioxide in your child’s body.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
There are two types of thanatophoric dysplasia characterized by how bones form:
Thanatophoric dysplasia is rare and occurs in an estimated 1 out of every 20,000 births.
Advertisement
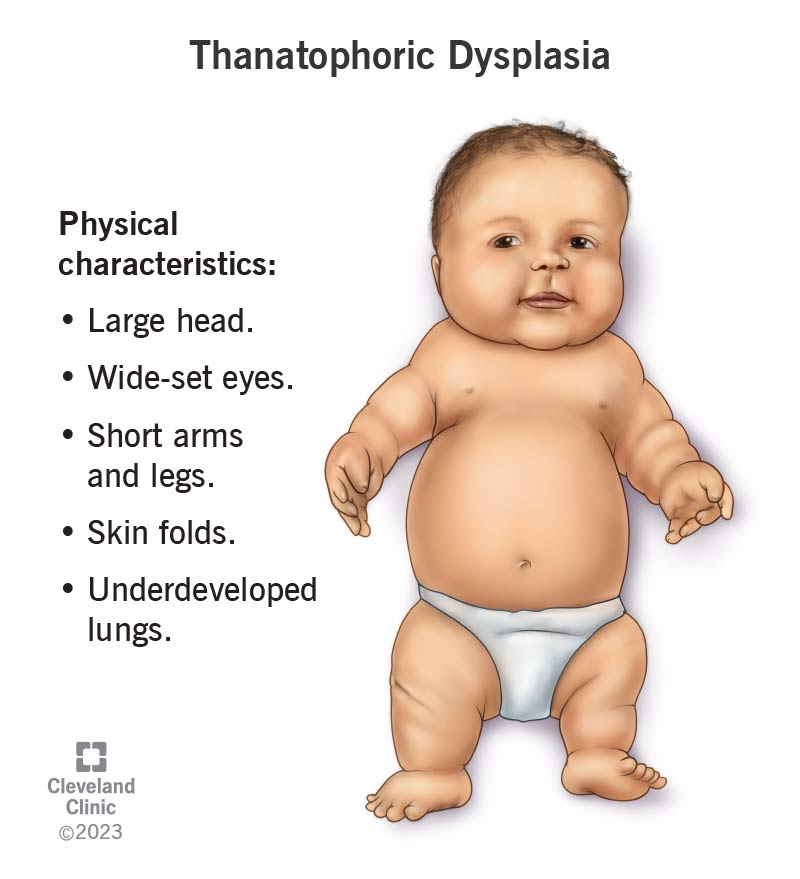
Thanatophoric dysplasia affects how a fetus’ lungs, bones and joints grow and develop in the uterus. This can lead to signs that include:
The leading cause of death among infants diagnosed with thanatophoric dysplasia is respiratory failure. This makes it difficult for a baby to breathe.
Babies who survive infancy may experience additional symptoms, including:
A mutation (genetic change) of the FGFR3 gene causes thanatophoric dysplasia. The FGFR3gene is responsible for giving the fetus instructions to develop and maintain bones. Your body tells this gene to do its job by turning on a light switch. A mutation of the FGFR3 gene permanently leaves the gene’s light switch to stay in the on position. When this occurs, the proteins that make up the gene are overactive. This limits the growth and formation of bones from cartilage (ossification) in the long bones of the body.
Almost all cases of thanatophoric dysplasia are due to a mutation in FGFR3 that’s new to the fetus and not inherited from a biological parent. It’s typically not present in a person’s biological family. While rare, the gene change can pass from one biological parent to a fetus in an autosomal dominant pattern.
Advertisement
Thanatophoric dysplasia can happen to any child, as the gene change happens randomly. Very rarely, a child could inherit the mutation from a biological parent.
Genetic changes aren’t the result of something a biological parent did while pregnant to cause the condition.
Diagnosis for thanatophoric dysplasia begins during pregnancy and is typically detected on prenatal ultrasounds. Your healthcare provider will offer tests to identify possible genetic conditions during pregnancy. They’ll look for symptoms during prenatal ultrasounds like too much amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus (polyhydramnios) and bone growth symptoms.
If your healthcare provider finds a mutation of the FGFR3 gene after a test, they’ll take steps to avoid potential pregnancy complications.
After your baby is born, an X-ray of your baby’s bones and an ultrasound of their internal organs, especially their lungs, may be ordered to determine if any treatment for breathing might be helpful.
During pregnancy, your provider will offer different tests to diagnose genetic conditions. These tests include:
Babies who survive birth will immediately receive treatment to support underdeveloped lungs. This helps them breathe better. Respiratory support could include:
Additional treatments alleviate symptoms of the condition, including:
While most babies diagnosed with thanatophoric dysplasia don’t survive, your care team will recommend resources and support to comfort you and your loved ones through this diagnosis. Grief counseling or bereavement counseling helps individuals cope with loss and navigate challenging experiences that accompany a loss. Mental health providers are available to help you navigate grief as well.
There’s no way to prevent thanatophoric dysplasia because it’s often the result of a new genetic mutation that occurs randomly. If you plan on becoming pregnant, talk with your healthcare provider about genetic testing to understand your risk of having a child with a genetic condition.
The prognosis (outlook) is poor for babies diagnosed with thanatophoric dysplasia. This is due to the underdevelopment of their lungs. Their life expectancy is short. Many babies are stillborn or don’t survive during their first few weeks of life.
Babies who survive undergo intensive care to support their lungs and stabilize their breathing. Ventilator use is necessary throughout childhood.
Losing a child is extremely difficult and painful. This outcome can have a significant impact on your emotional well-being and mental health. Support services are available for grieving parents and family members to cope with the loss.
Learning that your baby has thanatophoric dysplasia is challenging and difficult. Your care team will help you and your loved ones say goodbye. They’ll also provide follow-up care to make sure you and your family are doing as well as you can after the loss of your child.
If you feel sad, anxious, depressed or hopeless and are having a difficult time grieving the loss of your child, reach out to your healthcare provider. They can connect you to a mental health professional or a bereavement support group where you can share your feelings with others who’ve had similar losses. Surrounding yourself with a network of support can help you manage the grief you’re feeling.
If your child born with thanatophoric dysplasia has trouble breathing, has an irregularly fast heartbeat or their skin turns a blue, purple or a pale color around their lips, mouth and fingers, they’re showing signs of respiratory distress and a lack of oxygen. Call 911 (or your local emergency services number) or visit the emergency room immediately.
Even if you’ve done everything possible to have a healthy pregnancy, genetic changes can cause life-threatening complications, like thanatophoric dysplasia. During this challenging time, you may feel sad, angry, confused, overwhelmed or lost, so it’s important to surround yourself with support. You may find comfort in talking with a mental health professional or joining a support group. Your care team is available to answer all of your questions and help you come to terms with the loss.
Last reviewed on 01/03/2024.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy