An abrasion is an injury where your skin rubs off. It’s also known as a scrape. You might get an abrasion after tripping on an uneven sidewalk or falling off of your bicycle. Abrasions cause pain, skin discoloration and light bleeding. You can treat small abrasions at home by cleaning and covering your wound.
An abrasion is a scrape on your skin. This is a break in your skin that happens when your skin rubs off. It may bleed slightly and hurt. An abrasion often happens when something hits or drags against your skin (friction). Abrasions are usually accidental injuries. They only affect the outermost layers of your skin.
An abrasion is similar to using a piece of sandpaper to remove paint from an object. The rough surface of the sandpaper rubbing against the object removes layers of paint just as an abrasion removes some of your skin.
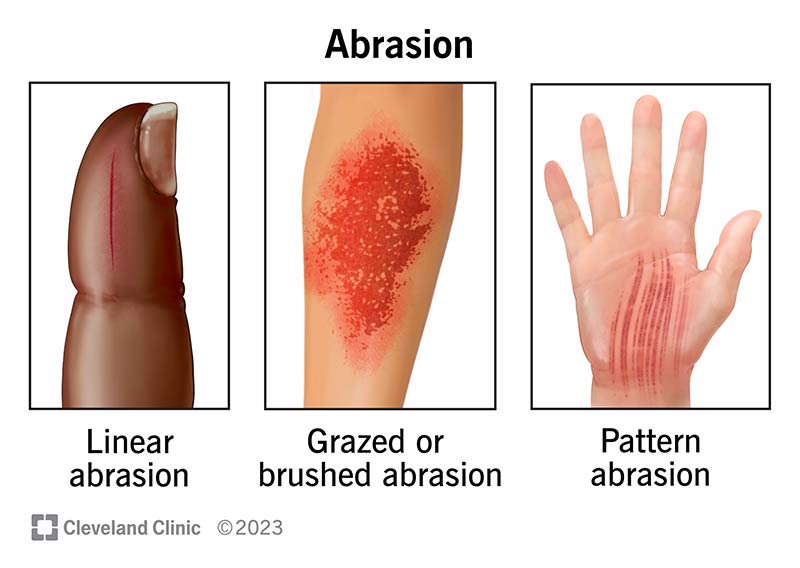
There are three types of abrasions:
Most of the time, an abrasion isn’t a serious injury. An abrasion usually only affects the top layer of your skin (epidermis) and doesn’t extend into deeper layers. While abrasions are common, they can lead to infections. Infection is a serious consequence of a wound.
An abrasion and a laceration are types of wounds. A wound is an injury to your skin and body tissues. An abrasion or scrape is a wound where an area of your skin rubs off. None of your skin is missing during a laceration. Instead, the wound breaks apart and separates the skin. Another word for a laceration is a cut.
Abrasions are very common. Everyone experiences minor abrasions during their lifetime. An abrasion is the most common childhood injury.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Symptoms of an abrasion include:
An abrasion is the result of your skin rubbing off. This may cause your injury to look:
Your skin may peel away from the abrasion area or the rubbed-off skin could clump together in an area of your injury. It’ll naturally fall off as your skin heals.
The most common areas where you’ll have symptoms of abrasions are on bony areas of your body, like your knees or elbows. You can get an abrasion anywhere on your skin. Abrasions are also possible in your eye (corneal abrasion) and in your mouth (dental abrasion).
Friction causes abrasions. Friction is the movement of a hard, uneven or rough surface, object or material against your skin. Common causes of abrasions include:
Advertisement
The most common complication of an abrasion is an infection. Symptoms of an infection include:
Since abrasions are the result of something rubbing against your skin, debris, dirt and contaminants can get into your wound. If not properly cleaned, bacteria from these contaminants can cause an infection.
If you notice signs of an infection, visit a healthcare provider. Infections can be serious if left untreated.
Most abrasions don’t need a diagnosis from a healthcare provider since they’re minor injuries that you can treat at home. In the event of an accident or serious injury, you may have a large abrasion that needs medical treatment. A healthcare provider will diagnose an abrasion by visually examining your wound. They’ll specifically note the following during the examination:
Your healthcare provider will take your complete medical history during a physical exam. They’ll also ask you questions about your symptoms, like:
These questions can help your healthcare provider offer treatment that’s best for your specific symptoms.
Advertisement
Treatment for an abrasion is proper wound care. You can do this at home by:
If you have a large abrasion or experience other symptoms or injuries, visit the emergency room immediately or contact 911 or local emergency services. You may need treatment with stitches for larger wounds.
A healthcare provider may offer a tetanus shot or antibiotics for abrasions caused by animals. This is a preventive form of treatment to reduce your risk of developing an infection. If you received an animal bite or scratch, visit a healthcare provider within 24 hours of the event.
Try to avoid picking at your abrasion as it heals. It can be tempting to rip off dead skin or scratch your wound. These actions can irritate the wound and delay your healing time. When you pick at your injury, you also put yourself at risk of getting bacteria into the wound and causing an infection.
Abrasions are usually accidental injuries. You can reduce your risk of getting an abrasion by:
Abrasions are usually minor injuries that heal quickly. Small abrasions (less than 2 inches) may heal without scarring, but larger abrasions can leave a scar or mark on your skin after your wound heals. Abrasions aren’t usually severe, but you can get an infection in a minor abrasion like a scrape if you don’t take care of your wound properly. A healthcare provider can treat larger abrasions and offer treatment to prevent infections.
Most abrasions heal within a week if they’re small (less than 2 inches). It could take up to two weeks or more for larger abrasions to heal.
Visit a healthcare provider if you have an abrasion that:
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Abrasions are very common injuries. Children are more at risk of developing abrasions because they’re still learning about how to safely navigate their environment. It can hurt to skin your knee after tripping on the sidewalk or falling off of a bicycle. You can treat minor abrasions at home. If you experience an abrasion that affects a large area of your body, visit the emergency room, your primary care provider or express care to receive treatment. They can also offer treatment to prevent infections, which are common complications of even minor abrasions.
Last reviewed on 06/16/2023.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy