Sleep deprivation is when you aren’t sleeping enough, or you aren’t getting good, quality sleep. When it’s severe or happens over an extended period, it can cause very disruptive symptoms that interfere with even the most routine activities. Long-term sleep deprivation can worsen many major health conditions. This condition is usually treatable.
Sleep deprivation is when a person doesn’t get enough sleep. This can be a short-term issue, affecting one or a few nights, or it can be a chronic concern that lasts weeks or even months. Sleep deprivation can happen for countless reasons, many of them harmless, but it’s also a key symptom of certain health conditions.
Sleep is something that everyone needs, and most people need a similar amount, depending on their age. That amount also changes with age. However, some people need more sleep to feel well-rested, while others need less, but these exceptions aren’t common. A change in your sleep patterns, gradual or sudden, is a reason to talk to a healthcare provider.
The average daily amount of sleep needed, by age, is:
Sleep deprivation can also take different forms. For some people, sleep deprivation happens because they stay awake instead of sleeping. For others, they’re still sleeping, but they aren’t getting quality sleep, so they still wake up feeling tired.
Sleep deprivation usually isn’t a major problem in limited, isolated amounts. However, research shows that chronic sleep deprivation can cause or contribute to a variety of health issues.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Insomnia and sleep deprivation are closely related but aren’t the same thing. Insomnia is when you’re unable to sleep when you try. Sleep deprivation is what happens when you don’t give yourself enough time to sleep don’t get enough sleep or both.
Sleep deprivation can happen to everyone at any point in their life.
Advertisement
Sleep deprivation is very common. Experts estimate between 50 million to 70 million adults in the U.S. meet the medical criteria for sleep deprivation at any point in time. Virtually every human being experiences sleep deprivation at some point in their life. For some people, it’s simply a greater or longer-lasting issue, or it happens for a more serious reason.
Your body needs sleep to regenerate certain systems and carry out certain processes. To understand more about that, it helps to know a little more about the human sleep cycle. That cycle involves different stages of sleep. Those are:
When you fall asleep, you typically enter stage 1 and then move in and out of stages 2 and 3. After that, you go into REM sleep and start dreaming. After the first REM cycle, you start a new sleep cycle and go back into stage 1 or 2. One cycle normally takes about 90 to 120 minutes before another begins. Most people go through four or five cycles per night (assuming they get a full eight hours).
Sleep deprivation has negative effects in multiple ways throughout your body. Those can affect the following body systems, organs and processes:
The effects of sleep deprivation depend on why it happens and how long it lasts. The longer a person has sleep deprivation, the greater — and more severe — the effects.
Sleep deprivation also increases your risk of developing certain conditions or making them worse if you have them. These conditions include:
Advertisement
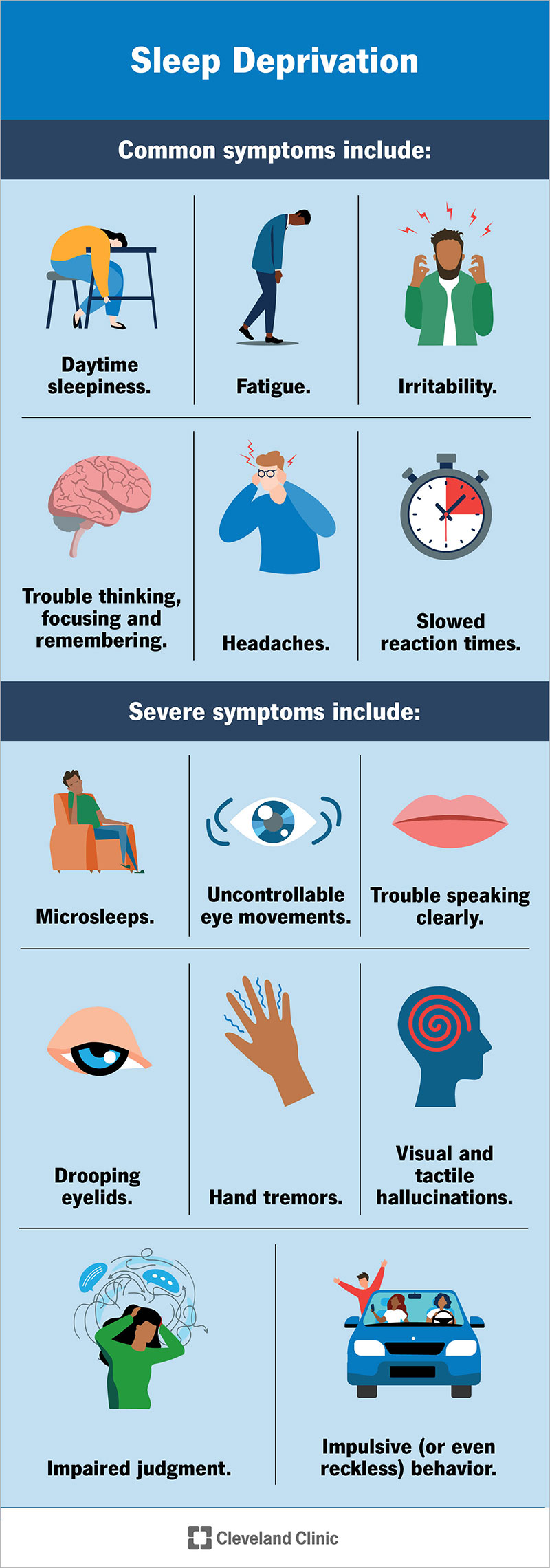
Sleep deprivation causes many symptoms. Some of the most common symptoms include:
As sleep deprivation goes on for longer, the symptoms become more severe. Many of the more severe symptoms look like the effects of alcohol intoxication. The severe symptoms of sleep deprivation include:
Total sleep deprivation, which is when you aren’t getting any sleep, happens in stages. These stages are:
Sleep deprivation can happen for numerous reasons. Many of these have to do with the circumstances of your life.
However, sleep deprivation can also happen for medical reasons. Some examples include:
Your mental health has a major impact on your sleep and vice versa. This can set up a cycle that reinforces itself as it gets worse. An example of this would be depression that makes it harder to sleep, which causes sleep deprivation, which then makes you feel even more depressed.
Mental health issues that can affect sleep include, but aren’t limited to, the following:
Sleep deprivation isn’t contagious. You can’t catch it from or spread it to others.
A healthcare provider can usually diagnose sleep deprivation simply by asking you questions about your symptoms, health history and your daily and nightly routines. However, there are a few conditions where further tests are needed to determine if a related condition is contributing to or happening because of sleep deprivation. Some possible tests include:
Other tests are also possible when sleep deprivation is something that your healthcare provider suspects. Your provider is the best person to tell you what tests they recommend and why they believe these tests are necessary.
Sleep deprivation can happen for many reasons, which means there’s no one way to cure it. Depending on why it happens, it’s often a treatable condition. However, treatment for sleep deprivation can take many different forms. Some treatment approaches focus on changing how a person sleeps (or prepares for sleep), while others focus on treating whatever disrupts a person’s ability to sleep.
Some of the more common treatments for sleep deprivation and related conditions include:
The possible complications and side effects vary depending on the treatment, the underlying cause of the sleep deprivation and other factors. Your healthcare provider is the best person to explain the complications or side effects that are possible or likely in your situation.
Sleep deprivation is a common issue, and often a person can manage it on their own. However, if the symptoms continue even with attempts to manage them on your own, you should talk to a healthcare provider. This is especially true if you have symptoms of sleep apnea, which is when you stop breathing in your sleep. That condition can cause severe or even life-threatening problems when it goes untreated.
The best things you can do to help treat and prevent sleep deprivation include:
The time it takes to recover from sleep deprivation depends on several factors, including how severe it is and how long it lasts. Most people can recover from sleep deprivation with only a few — or even just one — nights where they get enough quality sleep. However, some people may need several nights of quality sleep to recover from long-term sleep deprivation.
It’s possible to reduce the risk of developing sleep deprivation, but it’s virtually impossible to prevent it entirely. Because it can happen for so many reasons, many of which are normal and expected at some point in your life, everyone has some amount of sleep deprivation at some point.
To reduce the risk of having sleep deprivation, following the above recommendations on sleep hygiene, and ensuring you have enough time for an adequate amount of sleep can make a big difference. However, some causes of sleep deprivation are impossible to prevent or avoid, especially when it happens because of a medical condition.
In those instances, the best thing you can do is see your healthcare provider sooner rather than later. Early diagnosis and treatment, if necessary, can help minimize this issue’s effects and prevent it from causing more serious problems.
If you have sleep deprivation, the most likely effect you’ll notice is that you feel tired. As the amount of lost sleep increases, feeling tired becomes more noticeable and more severe symptoms will also appear. Eventually, people with severe sleep deprivation struggle to stay awake during the daytime, even while working.
As long as sleep deprivation continues, people with this issue will experience symptoms that can interfere with everyday routines and activities. There’s evidence that long-term or severe sleep deprivation can cause brain damage. There’s also ongoing research into whether or not a person can truly recover from sleep deprivation or if the effects are permanent. Currently, the available data suggests that it’s reversible with adequate sleep.
It’s also common for people with sleep deprivation to underestimate its impacts. Research shows that people with sleep deprivation often don’t realize how much the problem affects their brain, body and abilities.
Sleep deprivation lasts as long as a person isn’t getting enough sleep. This can be a single night or last for weeks, months or even years. If a person has sleep deprivation, they can recover by getting sufficient quality sleep. However, when sleep deprivation is severe or has lasted a long time, it can take multiple nights — or even up to a week — for a person to recover.
The outlook for sleep deprivation can vary, especially depending on why it’s happening, how severe it is and how long it lasts. It can also depend on your overall health, any other conditions you have and more. While sleep deprivation isn’t usually dangerous directly, it can put you in danger if you are so tired that it interferes with tasks that need your full attention, such as driving.
Fortunately, sleep deprivation is usually a very treatable condition. However, it’s important to discuss it with your healthcare provider if you notice it happening. While it’s easy to dismiss it and think it’s not a major problem, sleep deprivation can be an important clue that helps healthcare providers diagnose and treat an issue. It can also delay recovery from other conditions or make those conditions worse, so it’s important to talk about it with your healthcare provider.
If you have sleep deprivation, it’s important to work on improving your sleep. That includes getting enough sleep time-wise and ensuring that you’re getting quality sleep. The above tips on sleep hygiene can help, and your healthcare provider can also offer support and guidance to assist you.
You should see your healthcare provider if you have sleep deprivation along with sleep apnea symptoms. You should also see them if you have sleep deprivation that doesn’t get better, even with improvements in your sleep hygiene and habits.
Sleep deprivation isn’t a condition that causes immediate, life-threatening problems, so it doesn’t need emergency treatment. However, it can raise the risk of heart attack and stroke, both of which are emergency conditions that need immediate medical care.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Sleep deprivation is a condition that might seem minor, but it can have major negative effects on your activities and quality of life. It can also contribute to many other health conditions, some of which are dangerous over time.
If you have sleep deprivation, it’s important not to dismiss or ignore it. You can take many steps to improve your sleep, and if those aren’t successful, you should see your healthcare provider. They can determine whether or not you have sleep deprivation, how severe the issue is and why it’s happening, and then offer treatment recommendations. With timely diagnosis and treatment, getting the sleep you need is possible.
Last reviewed on 08/11/2022.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy