Sunburns occur from exposure to the sun’s UV rays or UV light from artificial sources. You can usually treat first- and second-degree sunburns at home. Third-degree sunburns are very rare but need emergency treatment. A sunburn can cause premature skin aging and skin cancer. You can lessen your risk of sunburn by taking steps to protect your skin.
Sunburn is red, painful, damaged skin from being out in the sun for too long. When you get a sunburn, ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun (or a tanning bed!) burn your skin. You don’t have to spend the day at the beach or pool to get a sunburn. Some people get sunburns doing everyday things without using sunscreen, like taking a lunch break outside, gardening or walking the dog.
Multiple sunburns can lead to premature skin aging and skin cancer. You can minimize your risk of sunburn by taking steps to protect your skin every day. It’s important to pay attention to your sun exposure when you spend any amount of time outdoors.
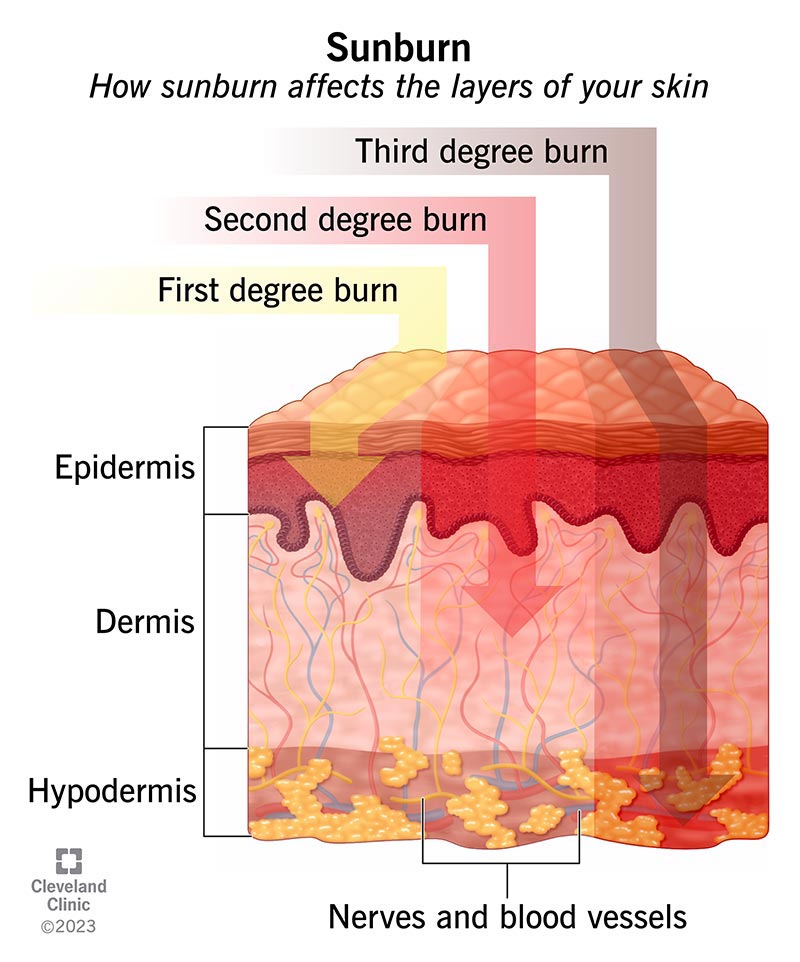
Healthcare providers group sunburns by the severity of skin damage. The two most common types of sunburn are:
A third-degree sunburn is very rare and requires emergency treatment. It severely damages all layers of your skin, including the fat layer beneath your skin. It can also destroy nerve endings. Most third-degree burns result from a chemical burn or a fire and not from sun exposure.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Sunburns are very common, especially in young people. Between 50% and 75% of children younger than 18 have sunburns each year. More than half of adults ages 18 to 29 reported having one or more sunburns in 2015.
If you get a sunburn, your skin might feel like it’s on fire — a hot and burning sensation that gets worse when you touch it, even with clothing.
Symptoms of sunburn depend on how severe your burn is. Symptoms may include:
You may also experience:
You may also experience symptoms of heat illness, including:
Advertisement
No sunburn is good. But a bad sunburn looks very red and inflamed. You may develop blisters and your skin will likely peel.
While others may notice your skin turning pink in the sun, unless you’re looking in a mirror, you probably won’t notice sunburn until the pain starts. Your sunburn will go through three stages:
Advertisement
Sunburn is caused by ultraviolet rays. There are two types of UV rays: UVA and UVB. Both types of rays can burn your skin.
Anyone can get a sunburn. But your chance of getting a sunburn increases depending on:
Your healthcare provider can evaluate the seriousness of your sunburn. They look at the amount of skin that’s burned, the severity of your sunburn and your symptoms. Then they can recommend the appropriate treatment.
You can treat most first- and second-degree sunburns by yourself at home. Steps you can take include:
If you have severe blistering or dehydration, your provider may give you rehydrating fluids.
If you have a third-degree sunburn, you may need a skin graft. A surgeon removes dead skin and transfers healthy skin from elsewhere on your body. These burns take weeks or longer to heal and can have severe complications.
You’re at a higher risk of sunburn if you:
You can prevent sunburn and lessen your risk of sun damage. Steps you can take include:
The good news is that the pain of sunburn doesn’t last long. Sunburns often go away on their own within a few days to a week. More severe sunburns take longer to heal. The bad news? The damage to the DNA in your skin cells is permanent. Each sunburn adds to your risk of developing skin cancer.
Frequent sunburns increase your risk of sun damage. Repeated exposure to harmful UV rays can cause:
See your provider if you have any concerns about your sunburn or how it’s healing. Seek medical treatment immediately if you have:
When your skin becomes sunburned, your skin’s blood vessels dilate, which leads to redness, inflammation and swelling. Your body sends immune cells to repair the damage. Some skin cells can be repaired and some die off. Others may have DNA mutations that can’t be fixed. These effects age your skin and can lead to skin cancer.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Sunburns are easy to get and hard to ignore. Even people who wear sunscreen can get sunburned, which is why it’s so important to reapply regularly. You can also add layers of protection: Wear a wide-brimmed hat, sunglasses and light-weight UV protective clothing. When you’re not slathering on cold lotion, you might feel like kicking yourself for ending up sunburned. But it happens to the best of us. Be sure to care for your sunburn and drink a lot of water while you heal. If you’re worried about a severe sunburn, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider.
Last reviewed on 06/07/2023.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy