Abnormal uterine bleeding is bleeding between monthly periods, prolonged bleeding or an extremely heavy period. Possible causes include fibroids, polyps, hormone changes and — in rare cases — cancer.
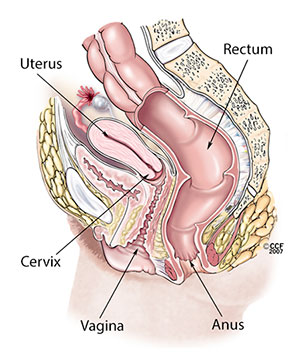
Abnormal uterine bleeding (formerly called menometrorrhagia) is when you bleed between your monthly periods or when your periods are extremely heavy and/or prolonged. Normal menstrual flow typically lasts about five days and occurs every 21 to 35 days.
Your provider should know about any abnormal bleeding you’re experiencing. What’s causing your bleeding may be harmless. But your bleeding may be a sign of cancer or conditions that may negatively impact your fertility.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Menometrorrhagia was once an umbrella term for two different conditions that sound nearly the same:
In 2011, the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) changed the names to prevent confusion. Menorrhagia is now called heavy menstrual bleeding. Menometrorrhagia is now called abnormal uterine bleeding.
The term “abnormal uterine bleeding” primarily describes bleeding in non-pregnant people in their reproductive years. But this doesn’t mean that irregular bleeding won’t affect you if you’re post-menopausal or pregnant.
If you’re bleeding and have experienced menopause, contact your provider. Bleeding after menopause is never normal. Blood may be red, pink, brown or even rust-like in appearance.
You should also contact your provider if you’re bleeding during pregnancy. Some causes are harmless, but others require medical attention, especially if the bleeding happens late in your pregnancy.
Advertisement
Not everyone who experiences abnormal uterine bleeding reports their symptoms. As a result, 10% to 35% of women worldwide may have abnormal uterine bleeding. But the numbers may be higher. It’s most common during menarche (when menstruation begins) and perimenopause (the years leading up to menopause).
Hormone imbalances are often to blame for abnormal uterine bleeding. They’re most common among people whose periods are just beginning or near ending.
The signs of abnormal uterine bleeding can vary. Some signs that your bleeding may be abnormal include:
Advertisement
Abnormal uterine bleeding can have many causes, including a variety of medical conditions and even stress:
Weighing more than your ideal body weight can lead to hormone imbalances that may cause abnormal uterine bleeding, too.
Forgetting to remove an IUD can lead to infection and abnormal bleeding. Trauma to your uterus, caused by an injury, can also cause bleeding.
Your healthcare provider will ask you several questions when working to diagnose abnormal uterine bleeding. These questions may include:
Your healthcare provider will then do a physical exam, including:
Your healthcare provider may order several tests or procedures when diagnosing abnormal uterine bleeding. These tests may include:
Your treatment depends on what’s causing your bleeding. Medications and surgical options are available to manage your bleeding or treat what’s causing it.
Medications used to treat abnormal uterine bleeding include:
There are several procedures available to treat abnormal uterine bleeding. Ask your provider about how often they perform a given procedure. Seeing a provider who frequently performs a procedure often leads to faster recovery with fewer complications.
You can’t prevent many causes of abnormal uterine bleeding. But you can reduce your risk of certain conditions that lead to abnormal bleeding. For instance, maintaining a healthy weight plays a potential role in keeping your hormones balanced. Avoiding diets that contain a high amount of animal fat can reduce your risk of some cancers. Practicing safer sex can reduce your risk of certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can cause abnormal uterine bleeding.
Your process for diagnosis and your options for treatment depend on what’s causing your bleeding. When making a diagnosis, your provider will consider multiple factors, including your age, symptoms, and risk factors for certain conditions that cause abnormal bleeding.
Your provider can individualize your care path – including diagnostic options and treatment — based on your physical exam and medical history.
Schedule an appointment with your provider if you’re noticing abnormal uterine bleeding so that they can address the underlying cause.
Symptoms to watch out for include:
If abnormal bleeding interferes with your quality of life, see your provider. You shouldn’t have to double up on menstrual products to manage your blood flow. You shouldn’t have to skip activities you enjoy or avoid going out in public because of heavy or unpredictable bleeding.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
You’re the best judge of what's normal for you — how long your periods usually last and how heavy your bleeding is. If your periods are especially heavy or lasting longer than usual, or if you’re bleeding outside your menstrual cycle, speak to your provider. You should never suffer in silence or be embarrassed. Many non-invasive treatment options are available to you that can provide relief from your bleeding.
Last reviewed on 11/11/2021.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy