The food you eat takes an incredible journey through your body, from top (your mouth) to bottom (your anus). Along the way the beneficial parts of your food are absorbed, giving you energy and nutrients. Here’s a step-by-step account of the digestive system’s workings.
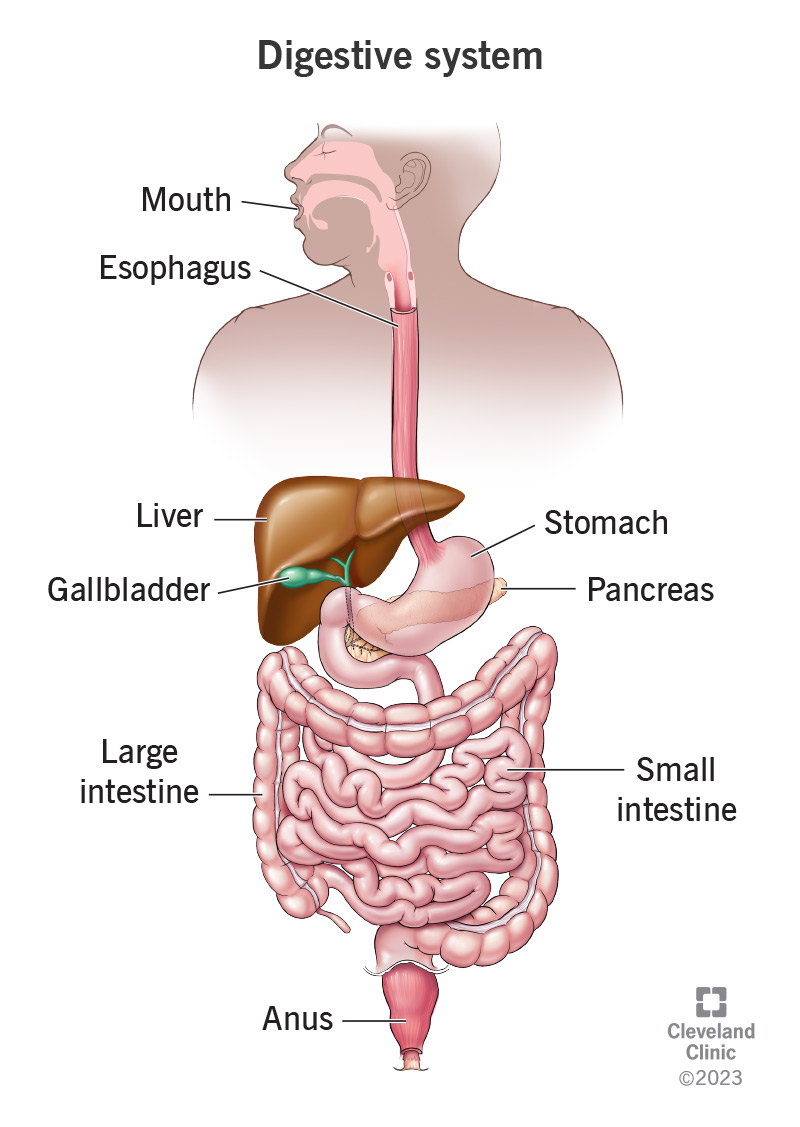
Your digestive system is a network of organs that help you digest and absorb nutrition from your food. It includes your gastrointestinal (GI) tract and your biliary system. Your GI tract is a series of hollow organs that are all connected to each other, leading from your mouth to your anus. Your biliary system is a network of three organs that deliver bile and enzymes through to your GI tract your bile ducts.
The organs that make up your GI tract, in the order that they are connected, include your mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and anus.
Your biliary system includes your liver, gallbladder, pancreas and bile ducts.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Your digestive system is uniquely constructed to do its job of turning your food into the nutrients and energy you need to survive. And when it’s done with that, it handily packages your solid waste, or stool, for disposal when you have a bowel movement.
Digestion is important because your body needs nutrients from the food you eat and the liquids you drink in order to stay healthy and function properly. Nutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and water. Your digestive system breaks down and absorbs nutrients from the food and liquids you consume to use for important things like energy, growth and repairing cells.
Advertisement
The main organs that make up your digestive system are the organs known as your gastrointestinal tract. They are: your mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and anus. Assisting your GI organs along the way are your pancreas, gallbladder and liver.
Here’s how these organs work together in your digestive system.
The mouth is the beginning of the digestive tract. In fact, digestion starts before you even take a bite. Your salivary glands get active as you see and smell that pasta dish or warm bread. After you start eating, you chew your food into pieces that are more easily digested. Your saliva mixes with the food to begin to break it down into a form your body can absorb and use. When you swallow, your tongue passes the food into your throat and into your esophagus.
Advertisement
Located in your throat near your trachea (windpipe), the esophagus receives food from your mouth when you swallow. The epiglottis is a small flap that folds over your windpipe as you swallow to prevent you from choking (when food goes into your windpipe). A series of muscular contractions within the esophagus called peristalsis delivers food to your stomach.
But first a ring-like muscle at the bottom of your esophagus called the lower esophageal sphincter has to relax to let the food in. The sphincter then contracts and prevents the contents of the stomach from flowing back into the esophagus. (When it doesn’t and these contents flow back into the esophagus, you may experience acid reflux or heartburn.)
The stomach is a hollow organ, or "container," that holds food while it is being mixed with stomach enzymes. These enzymes continue the process of breaking down food into a usable form. Cells in the lining of your stomach secrete a strong acid and powerful enzymes that are responsible for the breakdown process. When the contents of the stomach are processed enough, they’re released into the small intestine.
Made up of three segments — the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum — the small intestine is a 22-foot long muscular tube that breaks down food using enzymes released by the pancreas and bile from the liver. Peristalsis also works in this organ, moving food through and mixing it with digestive juices from the pancreas and liver.
The duodenum is the first segment of the small intestine. It’s largely responsible for the continuous breaking-down process. The jejunum and ileum lower in the intestine are mainly responsible for the absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream.
Contents of the small intestine start out semi-solid and end in a liquid form after passing through the organ. Water, bile, enzymes and mucus contribute to the change in consistency. Once the nutrients have been absorbed and the leftover-food residue liquid has passed through the small intestine, it then moves on to the large intestine (colon).
The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum that break down protein, fats and carbohydrates. The pancreas also makes insulin, passing it directly into the bloodstream. Insulin is the chief hormone in your body for metabolizing sugar.
The liver has many functions, but its main job within the digestive system is to process the nutrients absorbed from the small intestine. Bile from the liver secreted into the small intestine also plays an important role in digesting fat and some vitamins.
The liver is your body's chemical "factory." It takes the raw materials absorbed by the intestine and makes all the various chemicals your body needs to function.
The liver also detoxifies potentially harmful chemicals. It breaks down and secretes many drugs that can be toxic to your body.
The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile from the liver, and then releases it into the duodenum in the small intestine to help absorb and digest fats.
The colon is responsible for processing waste so that emptying your bowels is easy and convenient. It’s a 6-foot long muscular tube that connects the small intestine to the rectum.
The colon is made up of the cecum, the ascending (right) colon, the transverse (across) colon, the descending (left) colon, and the sigmoid colon, which connects to the rectum.
Stool, or waste left over from the digestive process, is passed through the colon by means of peristalsis, first in a liquid state and ultimately in a solid form. As stool passes through the colon, water is removed. Stool is stored in the sigmoid (S-shaped) colon until a "mass movement" empties it into the rectum once or twice a day.
It normally takes about 36 hours for stool to get through the colon. The stool itself is mostly food debris and bacteria. These “good” bacteria perform several useful functions, such as synthesizing various vitamins, processing waste products and food particles and protecting against harmful bacteria. When the descending colon becomes full of stool, or feces, it empties its contents into the rectum to begin the process of elimination (a bowel movement).
The rectum is a straight, 8-inch chamber that connects the colon to the anus. The rectum's job is to receive stool from the colon, let you know that there is stool to be evacuated (pooped out) and to hold the stool until evacuation happens. When anything (gas or stool) comes into the rectum, sensors send a message to the brain. The brain then decides if the rectal contents can be released or not.
If they can, the sphincters relax and the rectum contracts, disposing its contents. If the contents cannot be disposed, the sphincter contracts and the rectum accommodates so that the sensation temporarily goes away.
The anus is the last part of the digestive tract. It is a 2-inch long canal consisting of the pelvic floor muscles and the two anal sphincters (internal and external). The lining of the upper anus is able to detect rectal contents. It lets you know whether the contents are liquid, gas or solid.
The anus is surrounded by sphincter muscles that are important in allowing control of stool. The pelvic floor muscle creates an angle between the rectum and the anus that stops stool from coming out when it’s not supposed to. The internal sphincter is always tight, except when stool enters the rectum. This keeps us continent (prevents us from pooping involuntarily) when we are asleep or otherwise unaware of the presence of stool.
When we get an urge to go to the bathroom, we rely on our external sphincter to hold the stool until reaching a toilet, where it then relaxes to release the contents.
There are temporary conditions and long-term, or chronic, diseases and disorders that affect the digestive system. It’s common to have conditions such as constipation, diarrhea or heartburn from time to time. If you are experiencing digestive issues like these frequently, be sure to contact your healthcare professional. It could be a sign of a more serious disorder that needs medical attention and treatment.
Short-term or temporary conditions that affect the digestive system include:
Common digestive system diseases (gastrointestinal diseases) and disorders include:
If you have a medical condition, always ask your healthcare provider what you should do and eat to stay healthy and manage your condition. In general, the following are ways to keep your digestive system healthy:
Contact your healthcare provider if you are experiencing frequent symptoms such as constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain or cramps, excessive gas (farting), or heartburn. While most people experience these conditions every once in a while, if you experience them often, it could be a sign of a more serious digestive system issue.
Last reviewed on 08/09/2021.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy